Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Build a Basic Data Rehydration Pipeline
Completion Time: 10 Minutes
In this tutorial you'll learn how to create basic pipelines for telemetry data archiving and restoration using the Mezmo Archive Destination, the Pipeline Data Restoration Source, the Mezmo Log Analysis Destination, and JSON Demo Logs.
Prerequisites
You should have an S3 bucket that you can use as the archiving destination.
Pipeline Architecture
These two Pipettes illustrate the basic configuration of a Pipeline to send telemetry data to an S3 bucket, and then restore that data and send it to Mezmo Log Analysis.
Archive Pipeline
This Pipette sends Demo Log HTTP JSON data directly to a Mezmo Archive Destination for archiving in an S3 bucket.
For demonstration purposes this is a a two component Pipeline, but you would typically have processor groups for converting events to metrics or others to reduce log volume between the Source and the Archive Destination.
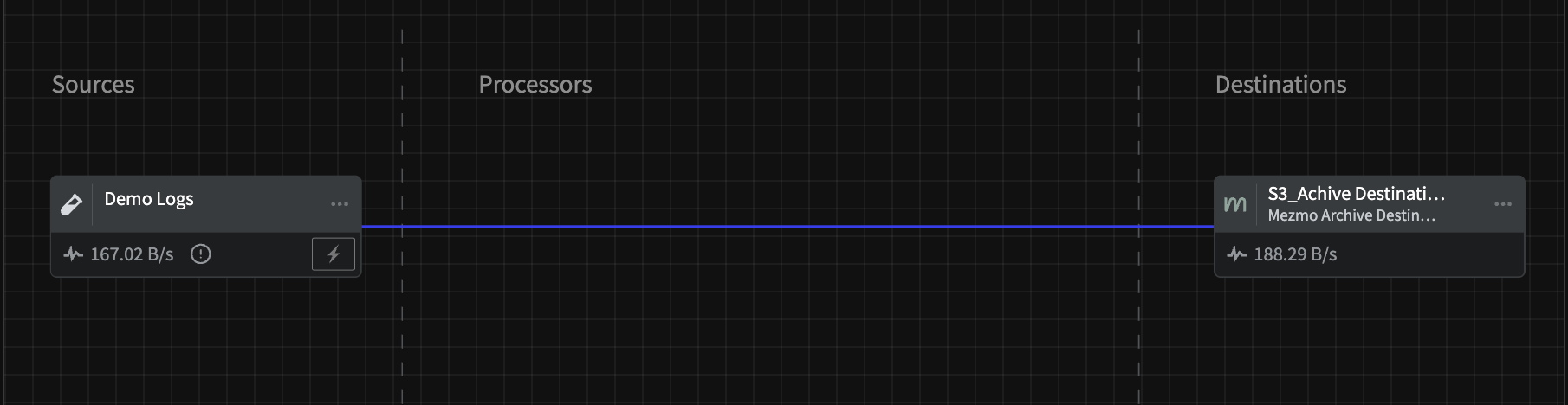
An example of sending data to an archiving destination.
Demo Logs Source Configuration
| Configuration Option | Settting |
|---|---|
| Interval (the number of seconds to pause between sending logs) | 1 |
| Format | JSON HTTP |
Mezmo Archive Destination Configuration
| Configuration Option | Setting |
|---|---|
| Batch timeout (seconds) | 300 |
| Archive Provider | S3 (note that you can also send archive logs to Azure) |
| Access Key ID | Access key for the S3 bucket |
| Secret Access Key | Secret access key for the S3 bucket |
| Bucket | The name of the S3 bucket |
| Region | The AWS region where the S3 bucket is located. |
Restoration Pipeline
This Pipeline sends archived data from the Pipeline Data Restoration Source, passes it through a Filter Processor to drop data and a Map Fields Processor to make sure that the restored data conforms to the required schema for the log analysis destination, and then finally sends it to Mezmo Log Analysis.
Note that this Pipeline is not active after being saved and deployed. Data will only begin to stream when the Pipeline is activated during a Restoration Task, described in the next section.
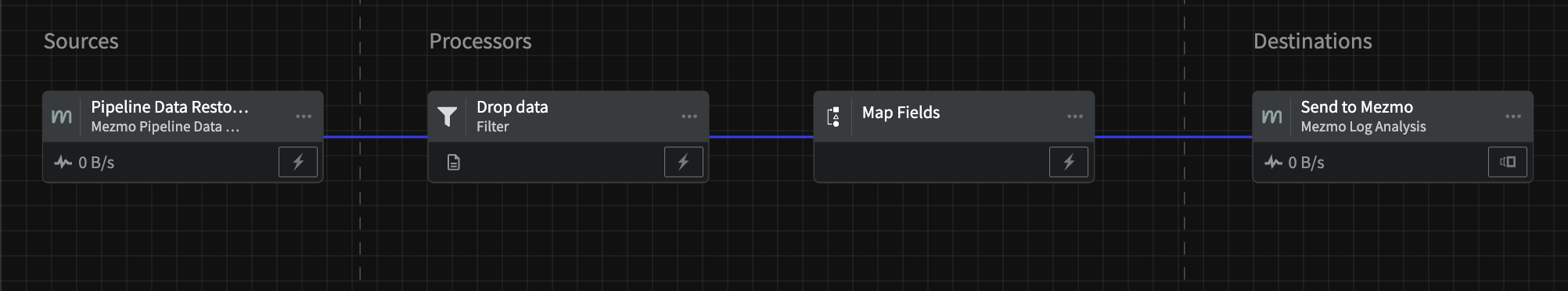
Mezmo Pipeline Data Restoration Source Configuration
There is no configuration for the Source other than giving it a Title. This is how you will identify where to send the data for the restoration task.
Filter Processor Configuration
This filter is set to only send a subset of the archived data to log analysis.
| Configuration Option | Setting |
|---|---|
| Action | Drop events matching this criteria |
| Conditional Statement | if (message.status greater_or_equal 200 AND message.status less 300) |
Map Fields Processor Configuration
This processor maps fields in the restored data to fields conform to the schema required for Mezmo Log Analysis.
| Source Field | Target Field |
|---|---|
message.method | message.line |
message.referrer | .app |
Mezmo Log Analysis Destination Configuration
The tags you enter in the configuration options are intended to help you easily search for restored data in in the Log Viewer.
| Configuration Option | Setting |
|---|---|
| Mezmo Host | logs.mezmo.com |
| Ingestion Key | The ingestion key for your Mezmo Log Analysis instance |
| Hostname | rehydrated-data |
| Tags (these will be attached to the restored data) | {{metadata.query.tags}} restored restored- data |
| Scheme | Message pass-through |
Create the Restoration Task
You must have admin privileges within your Mezmo Organization to create and run a restoration task.
You should create the restoration task in the same account that is associated with the restoration pipeline.
- In the Mezmo Web App, go to Settings > Archiving > Pipeline Restoration.
- Click New Pipeline Restoration Task.
- Enter a name for the restoration task.
- Enter the time period for the data you want to restore.
- Select the Pipeline Archive to restore data from.
- Select the Pipeline where you want to send the restored data.
- Click Start. You will see data begin to stream into the restoration pipeline, and then in your Mezmo Log Analysis viewer.