Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Metrics Data Optimization Pipeline
Step 1: Create a new Pipeline to handle and route OpenTelemetry Metrics
Create a new Mezmo Pipeline by clicking New Pipeline in the platform. Give this a name like Metric Handler, select Create Blank Pipeline, then select Continue at the bottom.
Step 2: Add OpenTelemetry Metric Source
Click Add Source and select your OpenTelemetry Metric source from the Shared Sources list similar to before.
Step 3: Insert State Enrichment
As we did with the previous pipeline, we will prepare the data to take advantage of Responsive Pipelines in the future by enriching each metric with the current pipelines operational state. Click the three dots on your Otel Metric Source and select Add Node->Add Processor->Script Execution.
Metric State Enrichment
Paste in the following Javascript and click Save. Note that the script does a bit more than add the operational_state state variable by tagging this data in-flight.
function processEvent(message, metadata, timestamp, annotations) { const state = getPipelineStateVariable("operational_state") message.op_state = state message.name = message.name.toString() message.tags.op_state = state metadata.resource.attributes["pipeline.path"] = "with_mezmo" if( message == null ){ return null } return message}Step 4: Route Based on State
After the initial Enrichment processor, let's route the data flow based on that operational_state. Connect a Route processor to the Enrichment Script with the following configuration:
- Title:
State Router - Route 1:
- Title:
Normal - Criteria:
message.op_statecontainsnormal - Route 2:
- Title:
Incident - Criteria:
message.op_statecontainsincident - Route 3:
- Title:
Deploy - Criteria:
message.op_statecontainsdeploy
You will end up with a pipeline that looks like the following
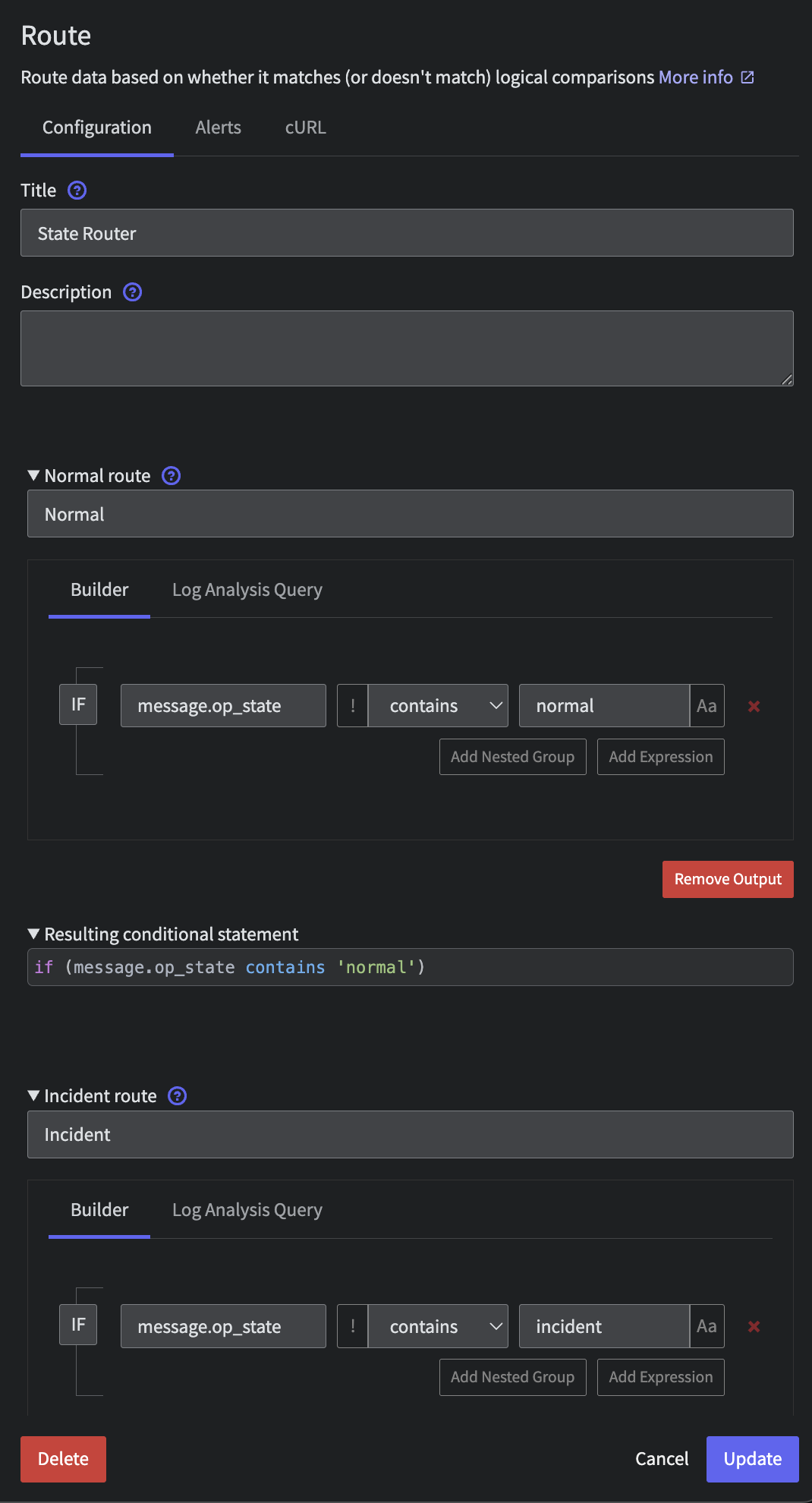
Metric State Router
Step 5: Normalize and Aggregate in Normal State
A common approach to reduce Metric data volumes is to aggregate those metrics and reduce their cardinality. Mezmo makes this incredibly easy with intuitive processors. We will implement a 5 min aggregation on all incoming metrics and trim off the tags being used. Connected to your Normal and Unmatched outputs from the State Router, add a Script Execution processor with the following script:
function processEvent(message, metadata, timestamp, annotations) { let service_name = message.tags.service_name let host_id = message.tags.host_id if( service_name == null ){ service_name = metadata.resource.attributes['service.name'] } if( service_name == null ){ service_name = 'NA' } if( host_id == null ){ host_id = metadata.resource.attributes['host.id'] } if( host_id == null ){ host_id = 'NA' } message.tags = { 'service_name': service_name, 'host_id': host_id } return message}Next, we will limit the cardinality of that host_id tag to 10 by connecting a Tag Cardinality Limit processor with the following configuration:
- Tags:
message.tags.host_id - Action:
drop_tag - Value Limit:
10 - Mode:
Probablistic
Finally, let's aggregate on a 5 min window by adding an Aggregate processor. Leave the default configuration, only changing the following:
- Interval (seconds):
300
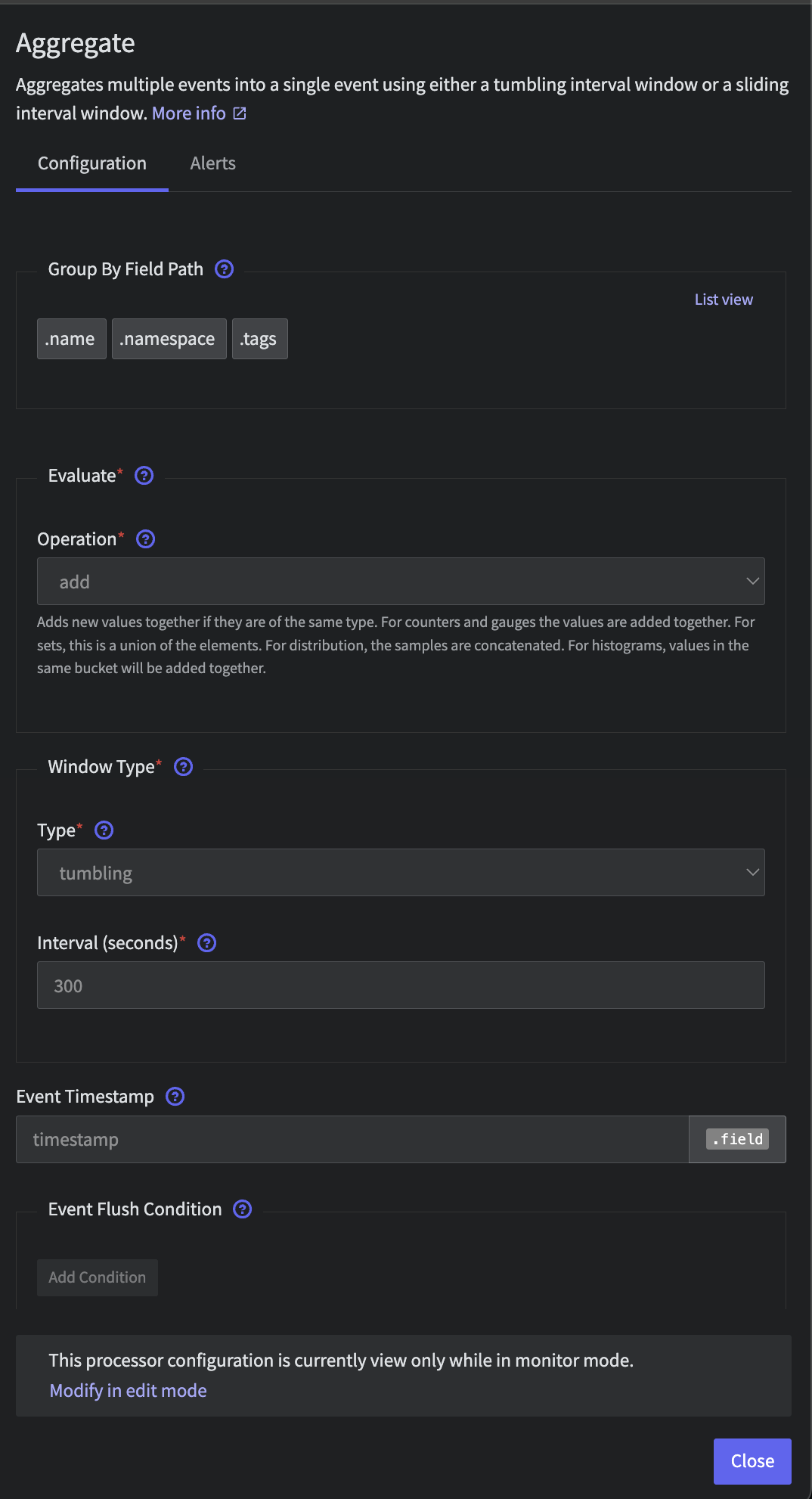
Metric Aggregator
Step 6: Sending Data Downstream Systems
Now, connect all outputs to a Blackhole destination. This is simply a placeholder for any Observability system you'd like. Explore our destinations in-app or in our docs to easily send telemetry data downstream into tools, data lakes and more.
You should have a pipeline that looks like the following.
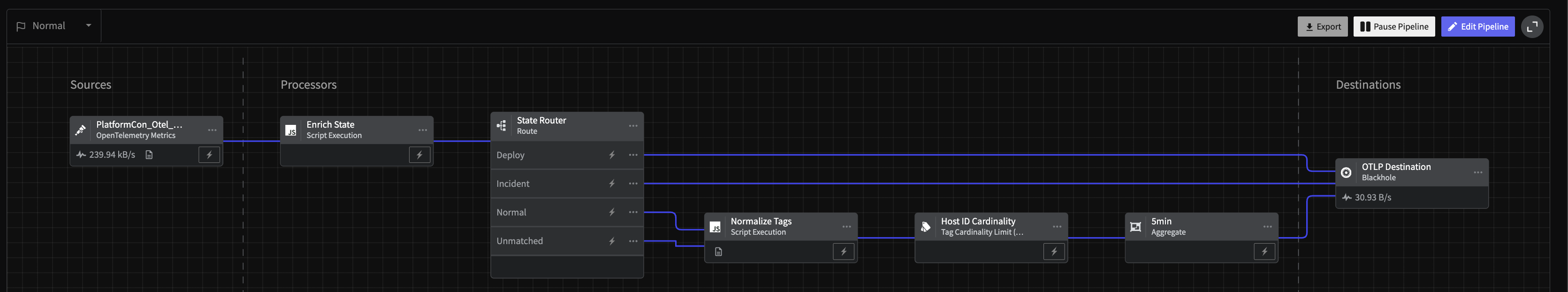
Metric Blackhole Connected
Step 7: Deploy
Finally, you must deploy your pipeline in order to start taking advantage of your metric optimizations.
Step 8: Initiate State and Grab State ID
Same as with the Logs, let's initiate the State and save the State ID of this pipeline for later.
First, flip the State in the UX from Normal to Incident and back to Normal to initialize.
Then, in your terminal window, run the following command with the metric pipeline's ID and grab that State ID.
curl --request GET \ --url 'https://api.mezmo.com/v3/pipeline/state-variable?pipeline_id=PIPELINE_ID' \ --header 'Authorization: Token PIPELINE_API_KEY'