Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Parse Processor
Description
With the Parse processor you can take incoming data of a known format and convert it into a parsed set of values prior to subsequent processing.
Use
The primary use case is for parsing logs sent to the HTTP endpoint. The labeled sources in the user interface are already parsed automatically.
You can create multiple parsing operations that will be performed in sequential order. This enables a stream of multiple logs to be separated without needing to build complex logic. If the first operation successfully parses all the incoming data, the Processor will exit to the next Pipeline component.
Configuration
There are two options for configuring the Parse processor.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Field | The JSON field to parse. Leave blank for the entire message. | .msg |
| Parser | The type of parser to use. | CSV |
Parser Options
| Parser | Description |
|---|---|
| Common Log | Also known as NCSA Common log format. This format is the basis for Apache Common Log and will work for Apache logs (not Apache Error logs however). |
| CSV | This formats comma separated values and makes the individual rows accessible as events where the key values within the parsed data are labeled with the columns. |
| Grok Pattern | This parser allows a user to define a grok expression for parsing unstructured data based on a desired output format. Note that the following literals are allowed between expressions, but otherwise you should use %{DATA} and %{GREEDYDATA} for data between expressions. Allowed literal characters: |
| JSON | This accepts any JSON that came in as a text string to make it explicitly JSON. Note that you might also need to use this if JSON is embedded within a message, such as inside of a syslog event. |
| Integer | Converts a string number into a numeric value. This can be used to parse hexadecimal, octal, and binary numbers into a base 10 format. |
| Query String | Takes any appended values from URL query parameters, meaning anything after the ? and parses them according to HTML character encoding |
| Regex Expression | This allows the user to enter a custom regular expression to be used in matching text within an unstructured text or line. Note that this is a special feature that must be turned on by request. Please try to use grok first as it is often a faster and safer way to extract data from unstructured text. |
| URL | Separates a URL into the individual components. |
| Tokens | This parser separates a string of words based on the contained whitespace and text references.
Note that the quotes and brackets can be escaped with a backslash ( |
| User Agent | This parser provides a best effort approach towards user agent identifiers, such as for browsers. It breaks the text of the user agent string into an object that can be subsequently used for processing. |
| Key/Value | This parser can be applied towards any text that includes a separated set of delimiters against a string. It includes:
This can be useful for |
| Timestamp | This parser allows you to define a parsing expression to be used against timestamp strings that are ingested within logs. Timestamp parsing expressions are evaluated based on the [strftime format](strftime format). Common preset expressions are included for ease of use. |
AI Pattern Matching
This Pipeline component is in Beta development, and should be used in Production environments with caution. Contact your Mezmo Account Manger to have this feature enabled. If you encounter any issues, please notify Mezmo Support.
The Parse Processor includes an AI feature that can generate a regular expression to use in parsing based on a sample of log data.
- Use the PIpeline Tap feature to collect a few sample logs that you want to parse in the pipeline, then paste the sample into the Sample log lines window.
- Click Find Patterns, and the AI assistant will generate the regex for that data sample.
- When you click Select Patterns, the regular expressions will be copied to the Expression field of the Parse processor. You can test and tweak these expressions in the Parse processor as necessary.
Mezmo uses a 3rd party LLM for generating regular expressions. Only your sample log lines are sent to a 3rd party LLM over API, please scrub any sensitive or user identifying data from your samples.
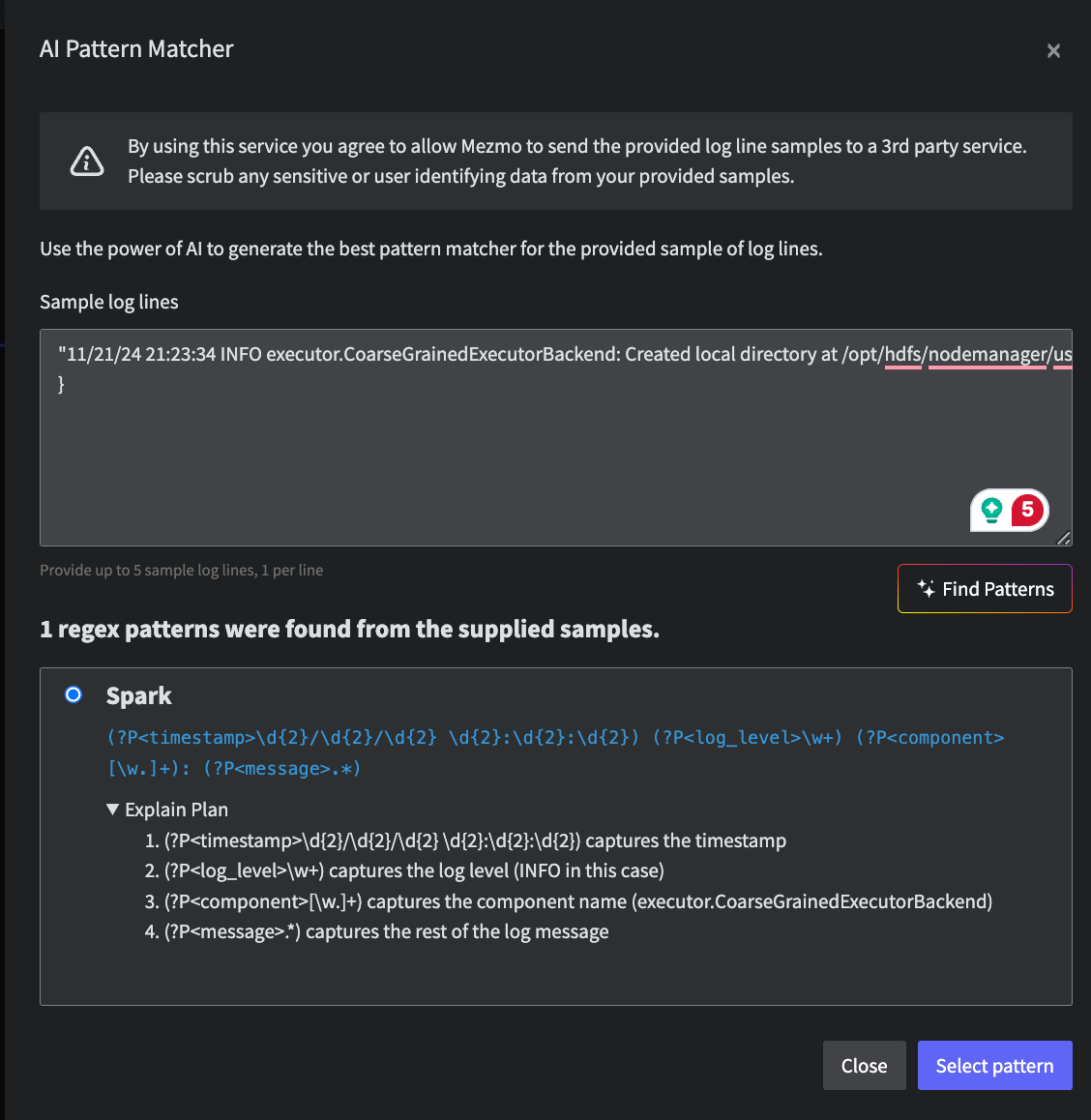
The AI pattern recognition interface for the Parse Process
Examples
Common Log
Input
91.227.35.153 - - [13/Feb/2023:23:23:03 +0000] "POST /js210dbc20e85d2c543d2cba57379ad20 HTTP/1.1" 200 9021Output
{ "host": "91.227.35.153", "message": "POST /js210dbc20e85d2c543d2cba57379ad20 HTTP/1.1", "method": "POST", "path": "/js210dbc20e85d2c543d2cba57379ad20", "protocol": "HTTP/1.1", "size": 9021, "status": 200, "timestamp": "2023-02-13T23:23:19Z"}Grok Pattern Example 1
Input
220.181.108.96 - - [13/Jun/2021:21:14:28 +0000] "GET /blog/geekery/xvfb-firefox.html HTTP/1.1" 200 10975 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Baiduspider/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)"Key items to note is that Mezmo does not support literals or regex values between grok patterns. This means that you will need to use the %{DATA} and %{GREEDYDATA} in replacing the literal characters.
You may still use a literal space %{SPACE} in between patterns and %{NOTSPACE} expressions in cases where the %{DATA} or %{GREEDYDATA} go to far.
Pattern used
%{IPORHOST:clientip} %{USER:ident} %{USER:auth}%{DATA}%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}%{DATA}%{WORD:verb} %{DATA:request} %{WORD}%{DATA}%{NUMBER:httpversion}%{DATA}%{POSINT:status} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}Output
{ "agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Baiduspider/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)" "auth":"-" "bytes":"10975" "clientip":"220.181.108.96" "httpversion":"1.1" "ident":"-" "referrer":"-" "request":"/blog/geekery/xvfb-firefox.html" "status":"200" "timestamp":"13/Jun/2021:21:14:28 +0000" "verb":"GET"}Timestamp
Input
Sat Jul 23 02:16:57 2005
Output
2005-07-23T02:16:57Z
User Agent
Input
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/109.0
Output
browser:{ family:"Firefox" version:"109.0"}device:{ category:"pc"}os:{ family:"Mac OSX" version:"10.15"}